Translate this page into:
Melanoacanthoma – A Diagnostic Dilemma
*Corresponding author: Iswarya Arumugam, Department of Dermatology, Sri Venkateshwaraa Medical College Hospital and Research Centre, Ariyur, Puducherry, India. iswarya2710@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Vijay V, Singh Y, David B, Arumugam I. Melanoacanthoma – A Diagnostic Dilemma. Indian J Postgrad Dermatol. 2024;2:57-9. doi: 10.25259/IJPGD_92_2023
Abstract
Melanoacanthoma (MA) is an uncommon benign tumour confined to the epidermis. It is formed by aggregation of pigment-producing melanocytes and keratinocytes. It is a close differential of melanoma and hence has to be evaluated in detail. Here, we present a case of MA over the scalp along with its clinical and dermoscopic description.
Keywords
Melanoacanthoma
Melanocyte
Malignant melanoma
Dermoscopy
INTRODUCTION
Melanoacanthoma (MA) is a benign, cutaneous epithelial tumour which comprises both pigment-producing melanocytes and keratinocytes.[1] The most common sites of predilections are the head, neck, trunk, extremities and ears. Oral mucosa and genital region may also be affected.[2] Although it is a rare condition, it poses a diagnostic dilemma due to its close resemblance to melanoma.[1] We present a case of MA with clinical, dermoscopic and histopathological description.
CASE DESCRIPTION
A 65-year-old male presented with a history of asymptomatic dark raised lesion over his scalp [Figure 1] for 20-year duration. The patient gave a history of slow progression of the lesion in size for the past 1½ years. He did not have any comorbidities. On local examination, a single, well-defined, hyperpigmented plaque of size 3 × 2 cm with a verrucous surface was seen over the left temporal region of the scalp [Figure 1]. Regional lymph nodes were not palpable. His routine blood investigations were within the normal limits. Dermoscopic (Heine’s 20T, non-polarised mode) examination showed comedo-like openings, fissures, crypts, cerebriform pattern and globular pattern [Figure 2]. A 3.5-mm punch biopsy from the edge of the lesion revealed marked acanthosis and focal hyperkeratosis of the epidermis with basaloid cells, spinous cells and scattered melanocytes with prominent melanin pigmentation and also a few pseudo horn cysts and true horn cysts [Figure 3]. The papillary dermis showed mild-to-moderate chronic inflammatory cell infiltration with pigment incontinence and melanophages.

- Dark raised lesion in the scalp.
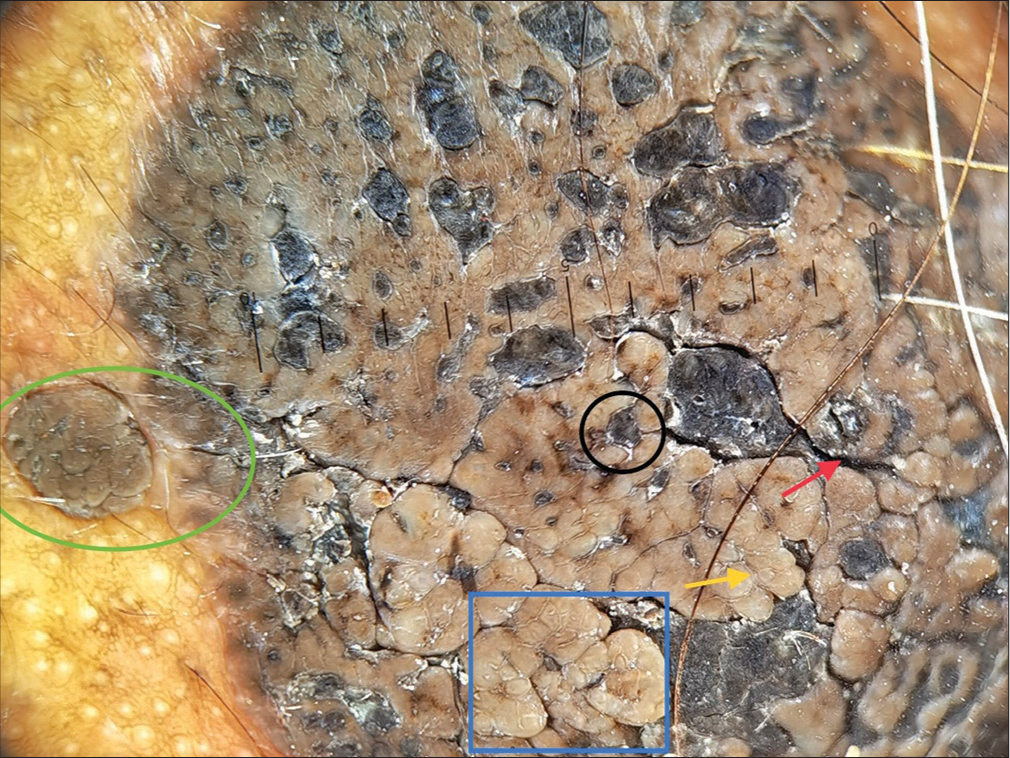

- Dermoscopy (Heine’s 20T, non-polarised mode) shows comedo-like openings (black circle), fissures (red arrow), crypts (yellow arrow), cerebriform pattern (blue box) and globular pattern (green circle).
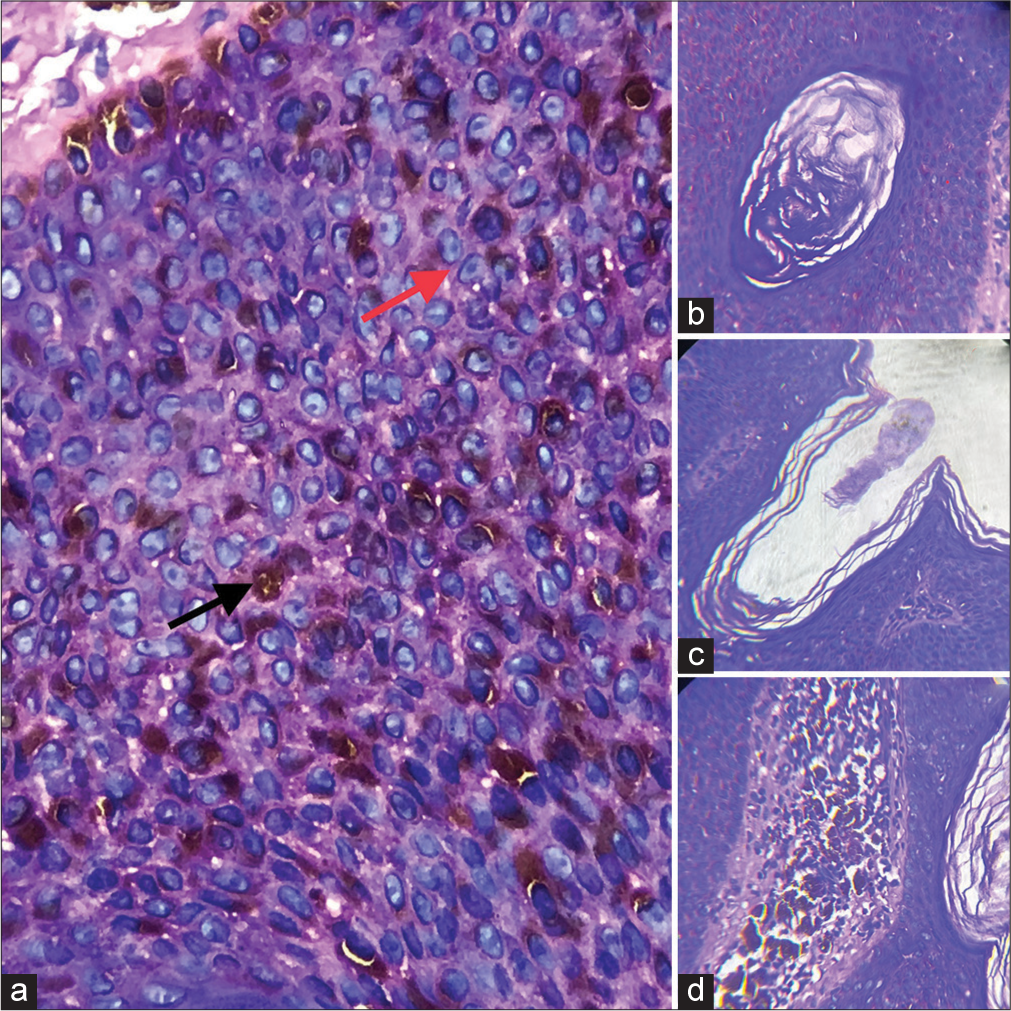
- (a) Haematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained section (×40 view) shows basaloid cells (red arrow) with scattered melanocytes (black arrow). (b) H&E section shows true horn cyst. (c) H&E section shows pseudo horn cyst. (d) H&E section shows scattered melanocytes.
DISCUSSION
MA is a rare variant of seborrhoeic keratosis. The lesion is composed of melanocytes and keratinocytes. It was originally described by Bloch in the year 1926 as non-nevoid melano-epithelioma.[1] He also designated it into type 1 and type 2 melano-epithelioma. Mishima and Pinkus introduced the term MA to illustrate the type 1 lesion and stated the type 2 lesion as pigmented seborrhoeic keratosis.
It commonly affects the elderly age group with no gender predilection. It is usually seen in light-skinned individuals.[1] It is an extremely rare condition with an incidence of only five in 5 lakh people.[1] It is usually asymptomatic in nature and presents as a solitary, flat or raised lesion. It can be present in the form of papule, nodule, plaque or horn.[1] When the lesions exceed more than 10 cm, it is considered as a giant MA. MA is the common imitator of malignant melanoma and pigmented seborrhoeic keratosis.[1] Both histopathology and dermoscopic features aid in the final diagnosis.
The dermoscopic features of MA include features of seborrhoeic keratosis such as comedo-like openings, milia-like cysts, moth-eaten border, fissures, crypts, hairpin vessels and cerebriform pattern.[3] However, melanoma-specific features such as blue-white veil, atypical dots, granularity and polymorphous vessels can also be seen in MA.[3] This emphasises the need for biopsy for confirmation of the diagnosis of MA and to differentiate it from malignant melanoma.
Histopathologically, two types of MA have been reported: (i) Diffuse and (ii) Clonal. A diffuse type, in which uneven scattering of melanocytes throughout the lobules of the tumour, and clonal type where melanocytes and keratinocytes are grouped in small nests. In our case, we described diffuse form in histopathology. The point differentiating MA from pigmented seborrhoeic keratosis is melanocytes that were restricted to the basal layer rather than being scattered.[4]
Treatment options for MA include local surgical excision that can be both diagnostic and therapeutic. Other treatment options encompass cryotherapy, laser ablation, and curettage. Complete removal of the lesion is required to prevent recurrence.[1]
CONCLUSION
A high index of suspicion is needed to prevent the misdiagnosis of MA that can easily masquerade melanoma.
Ethical approval
The research/study approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee at Sri Venkateshwaraa Medical College Hospital and Research Centre, number 25/SVMCH/IEC/-Cert/Aug 22, dated 25th August 2022.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using AI.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
References
- Melanoacanthoma Masquerading as Melanoma: Case Reports and Literature Review. Cureus. 2019;11:e4998.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oral Melanoacanthoma: A Report of 10 Cases, Review of the Literature, and Immunohistochemical Analysis for HMB-45 Reactivity. Am J Dermatopathol. 2003;25:12-5.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinical and Dermoscopic Features of Cutaneous Melanoacanthoma. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:1129-30.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Large Melanoacanthomas: A Report of Five Cases. J Cutan Pathol. 1984;11:309-17.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







