Translate this page into:
Collodion Baby Progressing to Camisa Syndrome: Case Report and Review of Literature in Asian Population
*Corresponding author: Saima Naaz, Department of Dermatology, Jawaharlal Nehru Medical College, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh, Uttar Pradesh, India. saimanaaz@outlook.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Naaz S, Adil M, Amin SS, Ahmed M. Collodion Baby Progressing to Camisa Syndrome: Case Report and Review of Literature in Asian Population. Indian J Postgrad Dermatol. 2024;2:92-4. doi: 10.25259/IJPGD_90_2023
Abstract
Palmoplantar keratoderma (PPK) is a broad entity comprising wide range of hereditary and acquired disorders. Herein, we present a case of 18-year-old female who presented with complaints of palmoplantar thickening since birth and progressive constriction bands around digits for 3 years. On examination, diffuse transgradient honeycomb type of PPK was present. Fibrous constriction bands (pseudoainhum) were present circumferentially around the distal interphalangeal joint of fifth finger and metatarsophalangeal joint of fifth toe bilaterally. Punch biopsy from palms revealed hyperkeratotic, stratified squamous epithelium with vacuolar degeneration and prominent keratohyaline granules. Audiogram was normal. On the basis of history, clinical examination and investigations, a diagnosis of Camisa syndrome was made and the patient was started on oral retinoids. We also discussed case findings of Camisa Syndrome reported in Asian population.
Keywords
Camisa syndrome
Palmoplantar keratoderma
Pseudoainhum
INTRODUCTION
Palmoplantar keratoderma (PPK) is a broad entity comprising wide range of hereditary and acquired disorders characterised by abnormal thickening of palms and soles.[1] Basic pathophysiology is compensatory epidermal hyperproliferation as a result of abnormal cornification of palmoplantar skin. PPK may present as an isolated entity or with associated cutaneous and systemic features.[2] We report a case of diffuse PPK presenting with generalised ichthyosis and pseudoainhum.
CASE REPORT
An 18-year-old unmarried female born to non-consanguineous marriage presented with complaints of palmoplantar thickening since birth and progressive constriction bands around digits for 3 years. On further inquiry, her parents revealed that she was born in a thin parchment like membrane which peeled off with time. Although photographic records of the same were absent. There was no history of hearing loss, mental retardation, periorificial keratotic plaques, alopecia, nail changes and loss of dentition. Family history was unremarkable. On examination, diffuse xerosis and flexural ichthyotic plaques were seen. Palms and soles revealed diffuse transgradient keratoderma with loss of dermatoglyphics resulting in a characteristic honeycomb pattern. Fibrous constriction bands (pseudoainhum) were present circumferentially around the distal interphalangeal joint of fifth finger and metatarsophalangeal joint of fifth toe bilaterally [Figure 1]. Examination of nails, teeth and oral mucosa revealed no abnormality. Haematoxylin and eosin-stained section from palmar skin revealed hyperkeratotic, stratified squamous epithelium with vacuolar degeneration and prominent keratohyaline granules [Figure 2]. Audiogram revealed no abnormality. Mutational analysis could not be performed due to financial constraints. On the basis of history, clinical examination and investigations, a diagnosis of Camisa syndrome was made. After informed consent, the patient was started on oral isotretinoin 20 mg once daily and was referred to plastic surgery for management of pseudoainhum. Response to treatment could not be assessed as the patient lost to follow-up.

- (a) Diffuse honey-comb type of palmar keratoderma extending proximally over wrist. (blue arrow). (b) Diffuse xerosis over dorsum of hands with glazed appearance of all the fingers and hyperkeratosis over proximal interphalangeal joints. (red arrow). Pseudoainhum involving the distal interphalangeal joints of 5th finger bilaterally (black arrows). (c) Diffuse plantar keratoderma with some sparing of the medial aspect of soles. (d) Pseudoainhum involving bilateral 5th toe (black arrows).
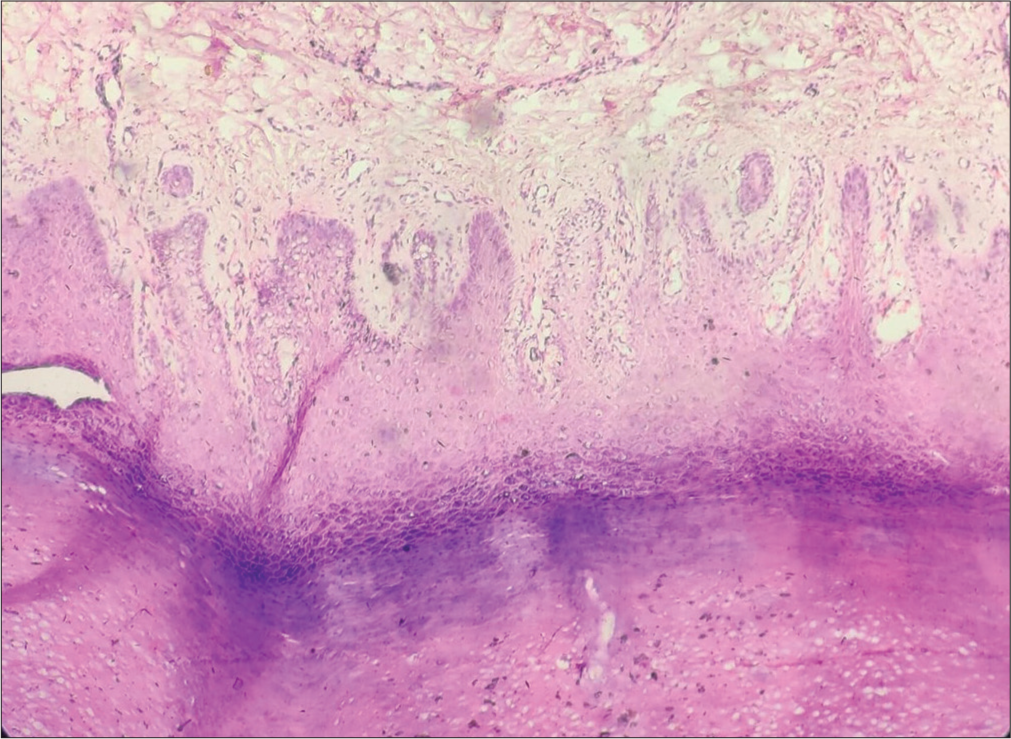
- Haematoxylin and eosin stained section (×100) of skin showing hyperkeratosis and prominent keratohyaline granules with perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate.
DISCUSSION
Camisa syndrome, also known as loricrin keratoderma, is an autosomal dominantly inherited genodermatosis caused by mutation in the LOR gene which encodes for loricrin, a major protein of cornified envelope.[3] It is characterised by diffuse PPK, generalised ichthyosis and pseudoainhum most commonly involving fifth digit.[3] Histological features include hyperkeratosis, focal parakeratosis, acanthosis, prominent keratohyaline granules, elongation of rete ridges and sparse dermal lymphocytic infiltrate with normal appendages.[3] Mutational analysis is advised for confirmation of diagnosis. Closest differential diagnosis for this presentation is Vohwinkel syndrome, caused by autosomal dominant mutation in GJB 2 gene encoding connexin 26. In addition to the above mentioned features, it is also characterised by sensorineural hearing loss and star fish shaped keratosis over knuckles.[3]
Other differentials to be considered in patients presenting with diffuse PPK and pseudoainhum are Mal-de-Meleda syndrome, Olmsted syndrome and Papillon-Lefevre syndrome. In Mal-de-Meleda, waxy, foul smelling PPK is preceded by persistent erythema while in Olmsted syndrome, periorificial keratotic plaques are present along with hair and nail changes.[2] Papillon-Lefevre syndrome is characterised by periodontitis.[2] However, none of the above syndromes feature collodion membrane as the presenting feature.
Management of Camisa Syndrome involves initiation of systemic retinoids, topical urea and salicylic acid combinations and surgical release of constriction bands in case of pseudoainhum.[3] Acitretin is usually the first-line systemic retinoid but isotretinoin can be preferred in women of child bearing potential.[3] In this case, we started with oral isotretinoin considering the cost of therapy and less duration of contraception (post-therapy).
Camisa syndrome mainly involves Caucasians and females.[3] There are heterogenous phenotypic presentations of the disease as only few pedigrees have been reported in literature.[1] As the disease is rare in Asian population, we did a literature search to review phenotypic presentation in this population. To the best of our knowledge, eight Asian families of Camisa syndrome have been reported [Table 1]. Pseudoainhum was present in seven of them with the fifth toe being most commonly involved.[3-9] Positive family history was noted in six out of eight families.[3,4,6,7,9,10] Yeh et al.[9] and Muñoz-Aceituno et al.[11] suggested that collodion baby may be the first presentation of this syndrome. We support this statement as our case also had a history of collodion baby at birth.
| S. No. | Author | Country | PPK | Ichthyosis | Pseudoainhum | Collodion baby | Family history |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Ali et al.,[4] 2006 | India | + | NS | Right 4thfinger | NS | + |
| 2. | Rajashekar et al.,[5] 2008 | India | + | + | Right great toe and 5thtoe bilaterally | NS | NS |
| 3. | Song et al.,[10] 2008 | China | + | + | - | NS | + |
| 4. | Yeh et al.,[9] 2013 | China | + | + | All fingers | + | + |
| 5. | Kura et al.,[6] 2014 | India | + | + | 5thtoe | - | + |
| 6. | Brar et al.,[7] 2015 | India | + | + | 5thfinger | - | + |
| 7. | Rout et al.,[8] 2020 | India | + | + | 5thtoe | NS | - |
| 8. | Baaniya and Agrawal,[3] 2021 | Nepal | + | + | 5thtoe | NS | + |
NS: Not specified, PPK: Palmoplantar keratoderma
CONCLUSION
This case highlights the importance of close follow-up of all collodion babies to diagnose the condition at the earliest as early recognition and treatment is of paramount importance to prevent complications such as pseudoainhum and resultant auto amputation.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval is not required.
Declaration of patient consent
Patient’s consent not required as patients identity is not disclosed or compromised.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using AI.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
References
- Palmoplantar Keratodermas: Clinical and Genetic Aspects. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2016;14:123-39.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereditary Palmoplantar Keratoderma: A Practical Approach to the Diagnosis. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2019;10:365-79.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exploring Pseudoainhum in Camisa syndrome. Clin Case Rep. 2021;9:e04995.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Variant of Vohwinkel's Syndrome. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2006;72:449-51.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camisa Disease: A Rare Variant of Vohwinkel's Syndrome. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2008;74:81.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reversal of Pseudo-ainhum with Acitretin in Camisa's Syndrome. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2014;80:572-4.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loricrin Keratoderma Presenting as Nonbullous Ichthyosiform Erythroderma: A Rare Case Report. Indian J Paediatr Dermatol. 2015;16:236-8.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Camisa Disease: A Rare Case Report. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2020;11:438-9.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collodion baby and Loricrin Keratoderma: A Case Report and Mutation Analysis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2013;38:147-50.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- A novel c.545-546insG Mutation in the Loricrin Gene Correlates with a Heterogeneous Phenotype of Loricrin Keratoderma. Br J Dermatol. 2008;159:714-9.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mild Collodion Baby as a Presenting Sign of Loricrin Keratoderma: Report of a Case and Review of the Literature. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2020;45:395-8.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







