Translate this page into:
Pemphigoid Gestationis in a Primigravida
*Corresponding author: Gajanand M. Antakanavar, Department of Dermatology, Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi, India. gajanand.hooli@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Antakanavar GM, Bahadur A, Kumar LP. Pemphigoid Gestationis in a Primigravida. Indian J Postgrad Dermatol. doi: 10.25259/IJPGD_258_2024
A 24-year primigravida with 8 months of pregnancy presented with multiple erythematous to urticated plaques associated with tense bullae over abdomen and extremities for 15 days. The patient had severe itching; however, it did not affect her sleep. There was no personal history of any skin disorders, allergies, taking any medications or fever. On examination, there were multiple erythematous and oedematous erythematous plaque studded with multiple papules and vesicles distributed at abdomen including periumbilical area, and bilateral lower limb and upper limb [Figure 1a and b]. There were multiple tense bullae present at both legs. The histopathological examination of the bullae (leg) revealed [Figure 1c and d] a large subepidermal blister filled with eosinophilic material. The infiltration of the surrounding tissue was characterised by a pauci-inflammatory response, predominantly consisting of lymphocytes, plasma cells and eosinophils, with no evidence of acantholysis. Antenatal ultrasonography was as per the gestational age. Final diagnosis of pemphigoid gestationis was made. Then, the patient had started on prednisolone 0.5 mg/kg/day along with oral antihistamines, which was lowered gradually over 4–5 weeks. The patient had significant relief in symptoms.
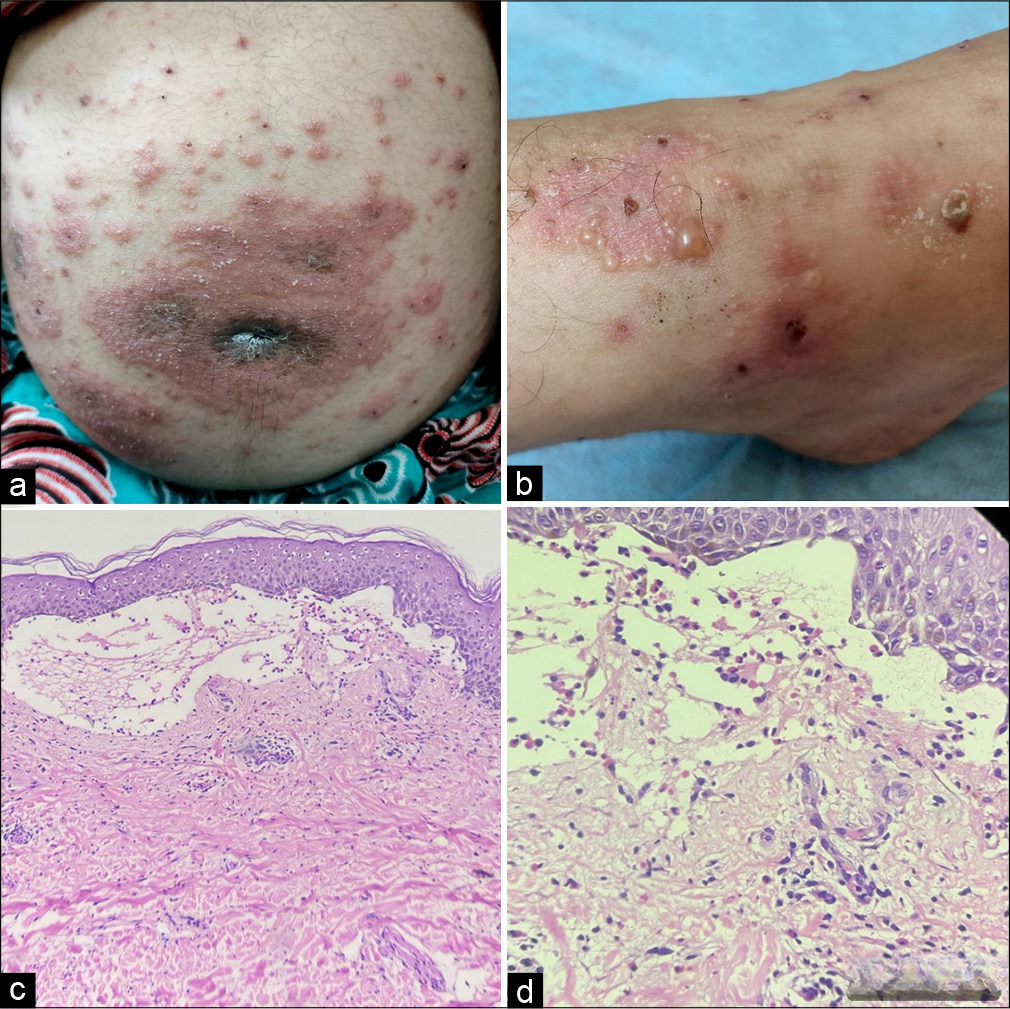
- (a and b) Multiple erythematous, urticated plaques with vesicles and bullae, predominantly distributed over the abdomen, with classic involvement of the periumbilical area and both lower limbs. (c and d) Histopathology image (Haematoxylin and Eosin stain ×100) subepidermal split which contains hyalin material along with few inflammatory cells consisting of lymphocytes, plasma cells and eosinophils (×400).
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval is not required.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using AI.
Financial support and sponsorship: Nil.







