Translate this page into:
Cutaneous Manifestations of Nutritional Deficiencies
*Corresponding author: Sahana Srihari, Department of Dermatology, Adesh Institute of Medical Sciences and Research, Punjab, India. drsahanasrihari@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Srihari S, Garg N, Iyer S. Cutaneous Manifestations of Nutritional Deficiencies. Indian J Postgrad Dermatol. 2025;3:27-9. doi: 10.25259/IJPGD_188_2024
INTRODUCTION
Proper nutrition is essential for the overall well-being of an individual. Insufficient intake of certain nutrients can lead to various health problems, including cutaneous manifestations.[1] This article aims to explore the different nutritional deficiencies that can affect the skin and their associated symptoms.
DISTINCTIVE SKIN CHANGES OF NUTRITIONAL DISORDERS AND SELECTED DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Changes in the skin can identify nutritional disorders affecting skin appearance [Figure 1]. This condition can be differentiated from other disorders such as exfoliative erythroderma, kwashiorkor, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis and staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome. Skin changes like phrynoderma may indicate deficiencies in Vitamins A, B-complex, C and essential fatty acids. Petechiae and purpura can be attributed to deficiencies in Vitamin K and C, as well as consumptive coagulopathy, coagulation disorders, thrombocytopenia, Ehlers–Danlos syndrome and cutaneous vasculitis like Henoch–Schonlein purpura. Yellow-orange discolouration may suggest carotenemia or jaundice, while hyperpigmentation may be caused by deficiencies in Vitamin B12, folate or Addison’s disease. Photo-distributed dermatitis can be a result of Vitamin B3 or B6 deficiencies, connective tissue diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus or dermatomyositis and polymorphous light eruption. Skin changes resembling seborrheic dermatitis may also indicate deficiencies in Vitamin B-complex. Angular stomatitis, angular cheilitis with candidal overgrowth and glossitis can be a sign of deficiencies in various vitamins, zinc, iron or underlying conditions such as Sjogren syndrome, oral lichen planus or syphilis. Diaper dermatitis might be associated with zinc deficiency or deficiencies in Vitamin B-complex. Lightening of hair can be due to malnutrition, copper deficiency or deficiencies in Vitamin B-complex. Poliosis or vitiligo may also cause changes in hair colour. Corkscrew hairs may suggest a deficiency in Vitamin C. Nail changes like koilonychia can be transient in young children or can be the result of iron deficiency or conditions like lichen planus, psoriasis or plummer vinson syndrome. Longitudinal hyperpigmented streaks on the nails may indicate deficiencies in Vitamin B3 or certain medications. Physiological factors, drug-induced side effects or trauma can also cause these nail changes [Tables 1 and 2].
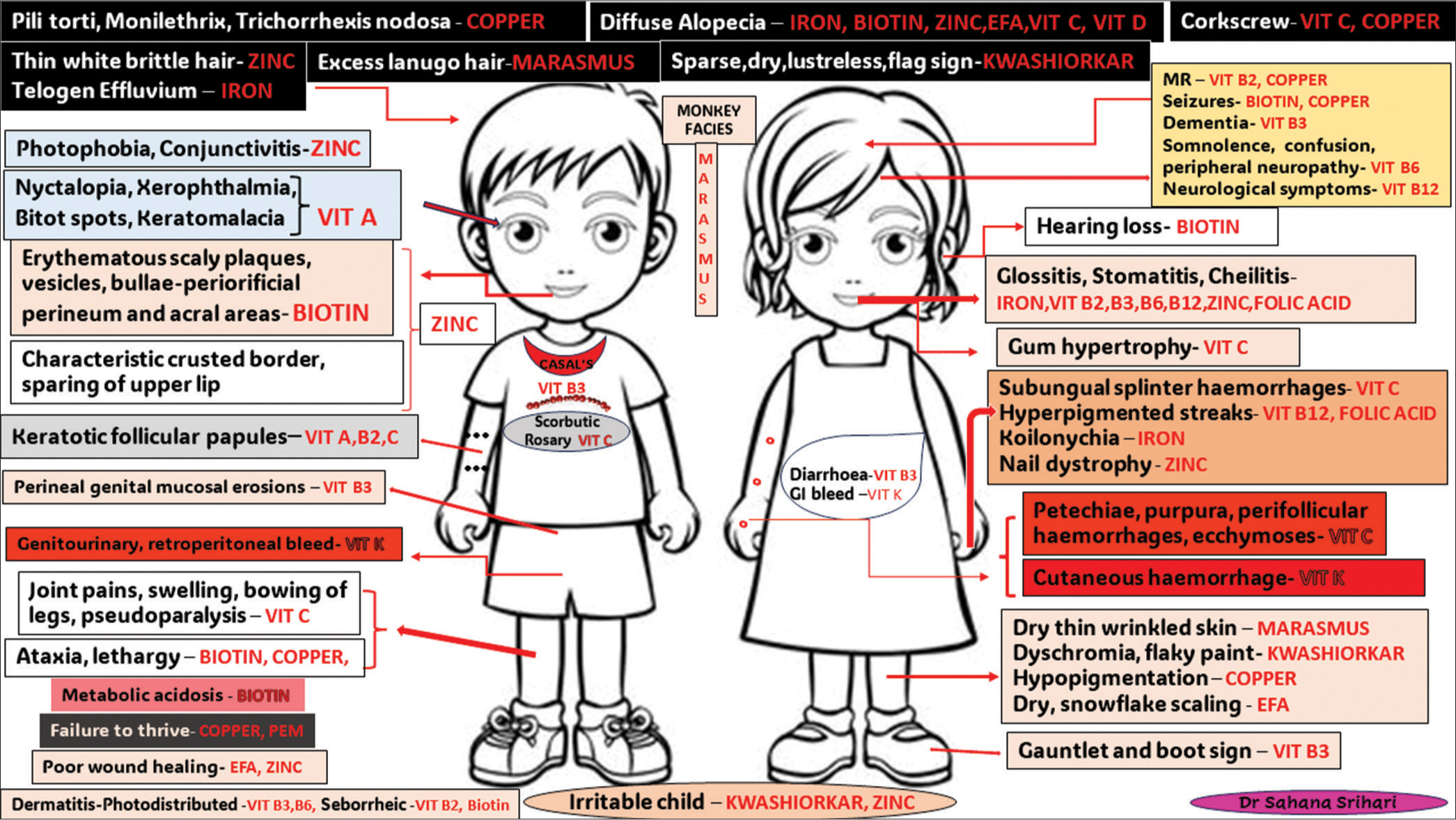
- Cutaneous manifestations of nutritional deficiencies. EFA: Essential Fatty Acids, GI: Gastrointestinal, PEM: Protein energy malnutrition, Vit: Vitamin.
| Vitamin A | Nyctalopia, xerophthalmia, bitot’s spots, keratomalacia, keratotic follicular papules |
| Vitamin B2 | Keratotic follicular papules, seborrheic dermatitis, glossitis, stomatitis, cheilitis |
| Vitamin B3 | Perineal genital mucosal erosions, diarrhoea, dermatitis-photodistributed, dementia, glossitis, stomatitis, cheilitis, casal’s necklace, gauntlet and boot sign |
| Vitamin B6 | Dermatitis-photodistributed, somnolence, confusion, peripheral neuropathy, glossitis, stomatitis, cheilitis |
| Biotin | Seborrheic dermatitis, diffuse alopecia, seizures, hearing loss, erythematous scaly plaques, vesicles, bullae-periorificial, perineum and acral areas, ataxia, lethargy, metabolic acidosis |
| Vitamin B12 | Hyperpigmented streaks on nails, neurological symptoms, glossitis, stomatitis, cheilitis |
| Vitamin C | Diffuse alopecia, corkscrew hairs, gum hypertrophy, subungual splinter haemorrhages, petechiae, purpura, perifollicular haemorrhages, ecchymoses, scorbutic rosary, keratotic follicular papules, joint pains, swelling, bowing of legs, pseudoparalysis |
| Vitamin D | Diffuse alopecia |
| Vitamin K | Gastrointestinal, genitourinary, retroperitoneal bleeding, cutaneous haemorrhage |
| Iron | Telogen effiuvium, diffuse alopecia, glossitis, stomatitis, cheilitis, koilonychias |
| Copper | Pili torti, monilethrix, trichorrhexis nodosa, ataxia, lethargy, failure to thrive, corkscrew hairs, mental retardation, seizures, hypopigmentation of the skin |
| Folic acid | Glossitis, stomatitis, cheilitis, hyperpigmented streaks on nails |
| Zinc | Thin white brittle hair, photophobia, conjunctivitis, erythematous scaly plaques, vesicles, bullae-periorificial perineum and acral areas, characteristic crusted border, sparing of upper lip, poor wound healing, diffuse alopecia, irritable child, glossitis, stomatitis, cheilitis, nail dystrophy |
| PEM | Failure to thrive |
| Kwashiorkar | Sparse, dry, lustreless hair, flag sign, irritable child, dyschromia, flaky paint dermatosis |
| Marasmus | Excess lanugo hair, monkey facies, dry thin-wrinkled skin |
| EFA | Poor wound healing, dry, snowflake scaling, diffuse alopecia |
PEM: Protein energy malnutrition, EFA: Essential fatty acids
| Differential diagnoses | |
|---|---|
| Vitamin B2 | Sjogren syndrome, oral lichen planus or syphilis |
| Vitamin B3 | Sjogren syndrome, oral lichen planus or syphilis, systemic lupus erythematosus or dermatomyositis and polymorphous light eruption, porphyrias, chronic actinic dermatitis, photosensitive drug eruptions and cutaneous lupus |
| Vitamin B6 | Sjogren syndrome, oral lichen planus or syphilis, systemic lupus erythematosus or dermatomyositis and polymorphous light eruption. |
| Vitamin B12 | Sjogren syndrome, oral lichen planus or syphilis, Addison’s disease |
| Vitamin C | Thrombocytopenia, Ehlers–Danlos syndrome and cutaneous vasculitis like Henoch– Schonlein purpura |
| Vitamin K | Thrombocytopenia, Ehlers–Danlos syndrome and cutaneous vasculitis like Henoch–Schonlein purpura, liver disease, inherited coagulopathies such as haemophilia, von Willebrand disease and Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome |
| Iron | Sjogren syndrome, oral lichen planus or syphilis, lichen planus, psoriasis, Plummer– Vinson syndrome |
| Folic acid | Sjogren syndrome, oral lichen planus or syphilis, Addison’s disease |
| Zinc | Sjogren syndrome, oral lichen planus or syphilis, psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis, irritant dermatitis |
| Copper | Myelodysplastic syndrome, cutis laxa, child abuse, osteogenesis imperfecta, Ehler–Danlos syndrome |
CONCLUSION
Hence, identifying such skin changes and the associated deficiencies is of paramount importance which needs a thorough knowledge of these manifestations.
In our article, we have summarised all the findings into a pictorial representation which would help the residents to remember them more easily.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval is not required.
Declaration of patient consent
Patient’s consent not required as there are no patients in this study.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using AI.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
References
- Skin Manifestations of Nutritional Deficiencies In: Rook A, Burns T, Breathnach S, eds. Rook’s Textbook of Dermatology (9th ed). United States: Wiley-Blackwell; 2016. p. :1234-56.
- [Google Scholar]







